What is CBD—the latest health craze? An alternative to prescription meds? Something else entirely? People are using it to manage stress, pain, anxiety and more. But is it a cannabinoid like THC? Can it get you high? Where does it come from? Is it safe? Or legal? For those questions and more we’ve assembled a comprehensive guide to explain how CBD works, what studies say so far, as well as guidance for finding quality products.
What is CBD? A cannabinoid named Cannabidiol.
That’s right, like THC, CBD is a cannabinoid—a type of compound produced by cannabis plants. Interestingly, our own bodies produce cannabinoids too. Ours are endogenously-produced cannabinoids which are referred to as endocannabinoids.
Cannabidiol, or CBD, was discovered in 1940. CBD isn’t as well known as THC—the most famous cannabinoid of all, but that’s changing. Unlike THC, CBD does not get you “high.” Cannabis and hemp plants produce something like 140 different cannabinoids. Of those, only THC can make you feel high.
So, there are cannabinoids produced by plants, and cannabinoids we produce internally called endocannabinoids. But, how do these compounds interact with our bodies? The answer to that mystery lies in a complex network called the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
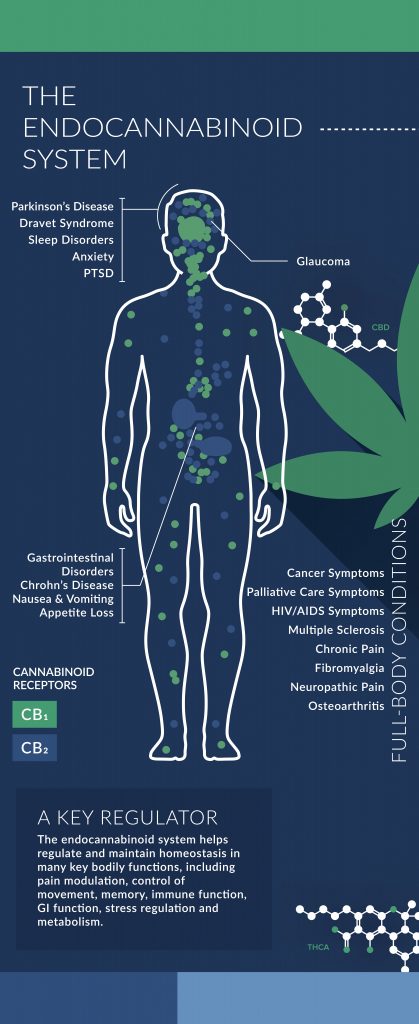 The endocannabinoid system branches out throughout our brains and bodies and is equipped with receptors, such as CB1 and CB2. These ECS receptors can interact with cannabinoids and endocannabinoids alike. The ECS is a homeostatic regulator that uses cannabinoids to adjust a broad variety of processes. In some cases, these adjustments include the dialing down of stress responses, inhibiting the release of inflammatory agents, or helping to boost anandamide signaling.
The endocannabinoid system branches out throughout our brains and bodies and is equipped with receptors, such as CB1 and CB2. These ECS receptors can interact with cannabinoids and endocannabinoids alike. The ECS is a homeostatic regulator that uses cannabinoids to adjust a broad variety of processes. In some cases, these adjustments include the dialing down of stress responses, inhibiting the release of inflammatory agents, or helping to boost anandamide signaling.
The ECS is the system that regulates all other bodily systems and processes. It’s the most important physical system you’ve never heard of. It regulates everything from immune system responses to sleep, appetite, mood, fertility and much more. As we’re discovering, the reason CBD seems to be able to have positive effects on such a broad number of conditions has to do with the fact that the ECS affects nearly everything in our minds and bodies. We’re also discovering that chronic inflammation, usually brought about by the body’s own inflammatory response, is the root of most disease. This is another reason CBD is effective for so many ailments. It’s a powerful anti-inflammatory and it acts on the ECS—which regulates all major bodily systems.
CBD is extracted from cannabis and hemp plants. Advances in cannabis processing in recent years has led to the popularization of extraction methods that eschew solvents in favor of heat, pressure or carbon dioxide. The result is an extremely clean extract called full-spectrum distillate which is used to make full spectrum CBD oil. The THC can be removed from the distillate to produce broad spectrum CBD oil. Next, CBD can be further isolated into pure CBD powder – referred to as CBD isolate. CBD isolate contains no THC and is used in products like Ethical Botanicals Hemp CBD Oil – No THC and CBD Oil for Pets.
Along with cleaner products have come more consistent ingestion methods and more accurate dosage. The use of CBD oil administered via measured dropper under the tongue has made it possible to easily measure out a desired dose.
How does CBD work?
It only became legal to research CBD in 2018, which means researchers have only just begun investigating this question. What we know so far is that CBD interacts with the ECS in a variety of ways, is a powerful anti-inflammatory and anti-anxiety agent, and promotes “homeostasis.”
Homeostasis is the condition of optimal functioning for organisms, a state of balance in which steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions are maintained.
CBD’s interaction with the ECS is crucial. The ECS is an incredibly complex system which regulates every other major bodily system. As a result CBD can impact a host of physiological processes and states, including mood, energy, digestion, immune activity, blood pressure, bone density, glucose metabolism, as well as how we experience pain, stress, hunger, and more. Cannabinoids, including our body’s own endocannabinoids, play the role of messengers in this system.
As endocannabinoid scientist Bradley E. Alger, (PhD, Harvard) describes them, “…Endocannabinoids are literally a bridge between body and mind.” This is why CBD seems to be able to affect so many conditions, because of the role it plays in the endocannabinoid system—which is connected to every system in your body.
In addition to this, studies indicate that CBD may help regulate how other chemicals naturally produced by our bodies are deployed. These include serotonin, which modulates mood and stress; adenosine, which plays a part in our sleep-wake cycle; and vanilloid, which is involved in pain modulation.
The ECS is critical to managing our bodily processes and ensuring that responses occur within reasonable limits. An overactive stress or pain response can de damaging or dangerous. When our ECS no longer functions properly, it can lead to chronic imbalances which lead to disease.
In fact, new research shows that most pathological conditions are the result of an unbalanced ECS. Thanks to discoveries like this, we are beginning to understand that “modulating endocannabinoid system activity may have therapeutic potential in almost all diseases affecting humans,” say Pal Pacher and George Kunos, scientists with the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), in a 2014 publication.
In some instances, CBD can help tip our ECS towards balance to slow or even stop disease progression. Charlotte Figi was afflicted with Dravet’s syndrome, which caused approximately 300 nearly-lethal seizures per day. Charlotte’s parents had already exhausted all pharmaceutical options before trying CBD. They tried a new CBD/THC product called Epidiolex. After starting on Epidiolex, Charlotte immediately went from having 300 nearly-lethal seizures per day, to just 1 or 2 mild ones per day.
Is CBD legal?
CBD oil has been 100% legal in Canada since 2018, consumers can own or take CBD freely.
One important thing to consider, however, is the presence of THC in some CBD products. This may be a concern for people who must submit to drug testing for sports or work. Full spectrum CBD oil contains trace amounts of THC. This means anyone with drug testing in their future should avoid full spectrum CBD oil and stick to Hemp CBD Oil – no THC.
As it matters to professional athletes, the World Anti-Doping Agency has removed CBD from its list of banned substances. It is legal for athletes in the US, UK and elsewhere to use CBD. However, THC is still banned. Therefore, athletes must ensure that the CBD products they consume do not contain THC.
Why are Canadians taking cannabidiol?
Although medical science has yet to catch up, millions of people have taken it and experienced improvements in their quality of life. This is evident from thousands of testimonials and product reviews online. We still lack scientific evidence for how well CBD works due to difficulty in conducting studies while CBD was illegal. But if you look online, you’ll find a mountain of anecdotal evidence out there that cannabidiol works.
Celebrities are helping drive awareness of cannabidiol’s benefits too. In fact, there have been a surprising number of celebrity endorsements. Everyone from supermodels like Alessandra Ambrosio to Olympic gold medalist Megan Rapinoe to pro golfer Bubba Watson to UFC star Nate Diaz has evangelized for CBD. In a few short years, awareness has risen and people have begun using it as a curative for the sick, as preventive medicine for the healthy, and as an all-purpose palliative for pets too.
What does the research on cannabidiol indicate so far?
Since the science around cannabidiol is still nascent, there isn’t that much information out there yet. However, with the wealth of studies currently underway, that will soon change. According to ClinicalTrials.gov, a US database of accredited clinical trials worldwide, at least 150 trials testing cannabidiol are currently in progress. It is being investigated as a treatment for a wide variety of health conditions, including autism, alcoholism, skin conditions and schizophrenia. But the problem of a lack of data is something researchers acknowledge and are eager to address.
“There is a great deal of interest in the possible therapeutic effects of CBD, but there is very little evidence of efficacy,” said Dr. J Hampton Atkinson, co-director of the Center for Medical Cannabis Research (CMCR) at the University of California, San Diego.
At the Center for Medical Cannabis Research, Dr. Atkinson suggested that there is “much interest in the possible anti-inflammatory effects of CBD, for use in arthritis of various types, including knees and hands,” Recent research on human cell lines with rheumatoid arthritis seems to suggest that cannabidiol may reduce inflammation.
There are other promising indicators too. Other studies indicate cannabidiol may reduce anxiety and self-deprecating thoughts. There’s also evidence CBD’s antipsychotic effects could help people with schizophrenia.
A 2017 clinical trial published in The New England Journal of Medicine found cannabidiol was highly effective in reducing seizures for people with Dravet’s syndrome. The list goes on.
 Can cannabidiol get you high?
Can cannabidiol get you high?
“CBD is the non-psychoactive portion of the plant, so what that means is you won’t have any effects like euphoria,” says Junella Chin, DO, an osteopathic physician and medical cannabis expert. “You won’t feel sedated or altered in any way.”
In short: No
CBD does not get you high.
Are there different kinds of CBD oil?
Indeed there are. The 3 main kinds are:
- Full Spectrum CBD Oil
- Broad Spectrum CBD Oil
- CBD Oil – No THC, made with CBD isolate.
First, full spectrum CBD oil. This oil is made from a raw extract containing hemp’s full spectrum of cannabinoids as well as other compounds like flavonoids and terpenes. The THC content of this extract is usually around 0.3% if it was taken from hemp. However, the THC content can be higher if the extract was taken from cannabis. When checking your CBD oil bottle ingredients, look for “full spectrum cbd distillate.”
Next, broad spectrum CBD oil is the same as full spectrum, the only difference being that the THC was removed. So you can think of this oil as THC-free full spectrum CBD oil.
Finally, CBD oil made with CBD isolate. This kind of oil has but 2 ingredients: 99.9% pure cannabidiol powder and a carrier oil. It can have many names like Hemp CBD Oil – No THC or just CBD Oil. To be sure, check the bottle ingredients to see if the CBD being used is indeed “CBD isolate.” This kind of CBD oil is most popular among people with THC sensitivities or those who many not be allowed to take THC for professional reasons.
What is the “entourage effect” all about?
Although more scientific research is needed to understand it fully, the “entourage effect” is the idea that cannabinoids and other compounds in cannabis plants work together to amplify healing effects. Research is preliminary at this point, so it is by no means definitive, but research from Israel suggests that whole-plant extract outperforms CBD isolate.
Some studies show that cannabidiol can actually reduce some of the psychoactive effects of THC. This means that when you choose a product that has both cannabidiol and THC, the cannabidiol may help curb unwanted effects like anxiety that some people experience when consuming high amounts of THC.
What are the benefits of cannabidiol?
One reason so many are turning to cannabidiol is because it is much easier on the body than the pharmaceutical drugs people are using to treat their conditions. Without the risk of addiction, plus almost no side effects, cannabidiol can be integrated into a regular self-care routine without harm.
If you listen to testimonials from friends or others, you’ll see that people are using cannabidiol in many different ways for many different reasons. Despite the fact that cannabidiol is not an approved treatment for many of the conditions people use it for, many people report that CBD has some sort of positive impact. Medical science has yet to determine whether these claims or true or not. But there is some promising research out there.
As more research comes online, we are getting a clearer picture of what CBD can really do and how it works. According to current research, cannabidiol might potentially, benefit people with a wide range of ailments, including:
- Autoimmune diseases (inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Neurological conditions (Alzheimer’s, dementia, Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, Huntington’s chorea, stroke, traumatic brain injury)
- Metabolic syndrome (diabetes, obesity)
- Neuropsychiatric illness (autism, ADHD, PTSD, alcoholism)
- Gut disorders (colitis, Crohn’s)
- Cardiovascular dysfunction (atherosclerosis, arrhythmia)
- Skin disease (acne, dermatitis, psoriasis)
Additionally, researchers are finding that CBD has neuroprotective effects. What’s more, research centers across the US and elsewhere are investigating its potential anti-cancer properties. In fact, a 2010 brain cancer study by California scientists found that cannabidiol “enhances the inhibitory effects of THC on human glioblastoma cell proliferation and survival.” This means that cannabidiol can enhance THC’s anti-cancer effects.
 Research has also shown cannabidiol to have anti-Alzheimer’s properties. In 2010, German researchers reported that cannabidiol stimulated neurogenesis, the growth of new brain cells, in adult mammals.
Research has also shown cannabidiol to have anti-Alzheimer’s properties. In 2010, German researchers reported that cannabidiol stimulated neurogenesis, the growth of new brain cells, in adult mammals.
Is CBD safe?
“I think CBD is a safe thing to try,” says Houman Danesh, MD, director of integrative pain management for the Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. According to the WHO, cannabidiol is generally well-tolerated in humans. it is non-toxic, non-addictive and you can’t overdose on it.
However, cannabidiol should be used like it is a medicine, not a supplement. Do not take cannabidiol while pregnant. If you are on any medication, speak to a health professional first as CBD can inhibit the uptake of certain medications in the same way that grapefruit does. For any serious health issues, it’s important to speak to your doctor before trying it for the first time.
What are the side effects of cannabidiol?
Like most things, if you overdo it, it can feel bad. Cannabidiol can cause some mild side effects, but it’s rare unless taking very large doses over 1500mg. The human body tolerates doses of CBD up to 1500mg very well, however, some side effects like tiredness, diarrhea, changes in appetite, insomnia, decreased appetite and fatigue can occur in the case of extremely high doses. To avoid experiencing any side effects, simply avoid taking doses far larger than what is recommended.
How do I take cannabidiol?
When beginning to take CBD for the first time, think of the following. What are you using it for? What is an appropriate first dose for someone of your weight? Do you prefer to feel the effects more quickly, or to feel them more slowly over a longer period of time? As cannabidiol is thought to be biphasic, different doses can make you experience different effects. Here are a few of the ways you can consume cannabidiol:
- Sublingually, which means drops of oil under the tongue.
- Vaping or smoking.
- Topical creams, balms or in bath bombs.
- Edibles like gummies or chocolates.
When cannabidiol is eaten in gummy or edible form, it must first pass through your digestive system before it reaches the bloodstream and eventually your endocannabinoid receptors. Your digestive system is quite efficient at scrubbing cannabidiol out, so a bit less gets into your system from edibles compared to a method like vaping or smoking. In addition, cannabidiol will take longer to reach your endocannabinoid receptors, but will stay in your body for a longer period of time, between four to eight hours.
Currently, the most popular way to take cannabidiol is sublingually—by putting a few drops of CBD oil under your tongue. Thanks to the large number of blood vessels there, it can be absorbed into your bloodstream without having to go through the digestive tract. This allows more to get into your system and for cannabidiol to reach endocannabinoid receptors more quickly.
Topical CBD creams are good to use for muscle and joint pain. Skin is not permeable to cannabidiol, but it can make it through the skin to local endocannabinoid receptors through pores. This means that you need a bit more of it in a cream if it is to get through the skin, so a higher potency skin cream is usually better. Cannabidiol is hydrophobic and it cannot travel through the body very easily. This means that CBD applied topically stays in the area where it was applied.
For more information about dosage, click here.
A few handy shopping tips
Here are a few handy tips to keep in mind when you’re shopping:
- Buy in the right kind of shop – no gas stations.
- Read labels carefully and check ingredients. Hemp oil, for example, contains no cannabidiol whatsoever.
- Avoid products made from hemp seed or stalks. Most of the cannabidiol is in the hemp flower.
- Look for bottles with measured droppers for convenient dose measurement.
- Make sure the products you buy have been 3rd party lab tested for quality.
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER
This site is for informational and educational purposes only. The information contained is not intended as medical advice, and cannot be used as a substitute for the medical advice of a physician or medical professional.

